Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) is a complex and potentially life-altering condition that affects millions of people worldwide. In this article, we'll explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for TBI, as well as strategies for recovery and rehabilitation.
What is Traumatic Brain Injury?
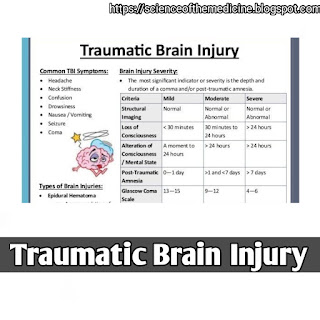
TBI occurs when the brain is damaged due to external forces, such as a blow to the head or a penetrating injury. The severity of TBI can range from mild to severe, with varying effects on cognitive, emotional, and physical functioning.
Causes of Traumatic Brain Injury
- *Falls*: Falls are a leading cause of TBI, particularly among older adults and young children.
- *Motor vehicle accidents*: Motor vehicle accidents can result in severe head injuries, including TBI.
- *Sports injuries*: Contact sports, such as football and hockey, can increase the risk of TBI.
- *Violence*: Physical abuse, domestic violence, and other forms of violence can result in TBI.
Symptoms of Traumatic Brain Injury
The symptoms of TBI can vary depending on the severity and location of the injury.
Common Symptoms
- *Cognitive symptoms*: Difficulty with memory, attention, and concentration.
- *Emotional symptoms*: Mood changes, irritability, and anxiety.
- *Physical symptoms*: Headaches, dizziness, and fatigue.
- *Behavioral symptoms*: Changes in behavior, such as impulsivity or aggression.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Traumatic Brain Injury
Prompt diagnosis and treatment are critical for optimizing outcomes after TBI.
Diagnostic Tests
- *Imaging tests*: CT scans and MRI scans can help identify structural damage to the brain.
- *Neuropsychological tests*: These tests assess cognitive and emotional functioning.
Treatment Options
- *Mild TBI*: Rest, pain management, and cognitive rehabilitation.
- *Moderate to severe TBI*: Hospitalization, surgery, and intensive rehabilitation.
Rehabilitation and Recovery
Rehabilitation and recovery from TBI require a comprehensive and individualized approach.
Rehabilitation Strategies
- *Cognitive rehabilitation*: Strategies to improve memory, attention, and concentration.
- *Physical therapy*: Exercises to improve mobility, strength, and balance.
- *Occupational therapy*: Training to improve daily functioning and independence.
- *Speech therapy*: Strategies to improve communication and speech.
Long-Term Effects of Traumatic Brain Injury
TBI can have long-term effects on cognitive, emotional, and physical functioning.
Potential Long-Term Effects
- *Cognitive difficulties*: Persistent problems with memory, attention, and concentration.
- *Emotional challenges*: Ongoing mood changes, irritability, and anxiety.
- *Physical limitations*: Persistent headaches, dizziness, and fatigue.
Conclusion
Traumatic Brain Injury is a complex condition that requires prompt diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for TBI, individuals can better navigate the recovery process and optimize outcomes.
Additional Tips
- *Seek medical attention*: If you suspect someone has a TBI, seek medical attention immediately.
- *Follow treatment plans*: Adhering to treatment plans can help optimize recovery.
- *Stay patient*: Recovery from TBI can be a long and challenging process.
- *Seek support*: Connecting with support groups and resources can help individuals and families cope with TBI.
By following these tips and staying informed, individuals can better understand and manage TBI, promoting optimal recovery and rehabilitation.
.jpeg)

