Introduction
Chicken pox, also known as varicella, is a highly contagious viral infection that affects people of all ages. Here's a comprehensive guide to chicken pox, covering its causes, symptoms, treatment, and prevention.
Causes
1. *Varicella-zoster virus*: Chicken pox is caused by the varicella-zoster virus, which is highly contagious.
2. *Transmission*: The virus can be spread through direct contact with an infected person's rash, saliva, or mucus.
3. *Airborne transmission*: The virus can also be spread through the air when an infected person coughs or sneezes.
Symptoms
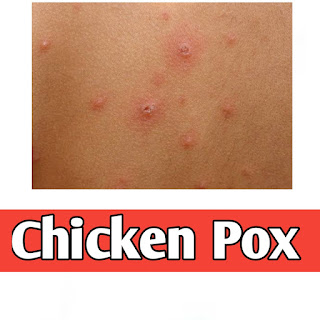
1. *Rash*: A characteristic rash appears, which progresses from red spots to blisters and eventually crusts over.
2. *Fever*: A fever often accompanies the rash.
3. *Fatigue*: Feeling tired and weak is common.
4. *Loss of appetite*: Decreased appetite can occur.
Stages of Rash
1. *Red spots*: The rash starts as red spots that develop into blisters.
2. *Blisters*: Blisters fill with fluid and eventually crust over.
3. *Crusting*: The blisters crust over and scab.
Treatment
1. *Antiviral medications*: Antiviral medications, such as acyclovir, can help reduce the severity and duration of symptoms.
2. *Symptomatic relief*: Over-the-counter medications, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, can help relieve symptoms like fever and itching.
3. *Rest*: Getting plenty of rest can help the body recover.
Complications
1. *Bacterial infections*: Secondary bacterial infections can occur.
2. *Pneumonia*: Chicken pox can lead to pneumonia, especially in high-risk individuals.
3. *Encephalitis*: Rarely, chicken pox can cause encephalitis, an inflammation of the brain.
Prevention
1. *Vaccination*: The varicella vaccine is highly effective in preventing chicken pox.
2. *Good hygiene*: Practicing good hygiene, such as frequent handwashing, can help prevent the spread of the virus.
3. *Avoiding contact*: Avoiding contact with infected individuals can help prevent transmission.
High-Risk Groups
1. *Pregnant women*: Pregnant women who are not immune to chicken pox are at higher risk for complications.
2. *Newborns*: Newborns whose mothers are not immune to chicken pox are at higher risk for complications.
3. *Immunocompromised individuals*: Individuals with weakened immune systems are at higher risk for complications.
Conclusion
Chicken pox is a highly contagious viral infection that can cause significant discomfort and complications. By understanding its causes, symptoms, treatment, and prevention, individuals can take steps to manage their symptoms and prevent transmission.
Additional Information
1. *Vaccination schedule*: The varicella vaccine is typically given to children in two doses.
2. *Post-exposure prophylaxis*: In some cases, post-exposure prophylaxis may be recommended to prevent chicken pox in high-risk individuals.
By prioritizing education and awareness about chicken pox, individuals can take steps to prevent transmission and manage their symptoms effectively.
.jpeg)

